A TWO AXIS SOLAR TRACKING SYSTEM TO TRACK SUN RAYS
Overview
A mechanical solar tracking structure that automatically moves solar panels to follow the sun throughout the day and across seasons.
Problem
Most solar plants use fixed panels or single-axis trackers that only follow the sun from east to west. This reduces energy generation because the sun’s position also changes north-south during the year. Existing dual-axis trackers can solve this but are complex, heavy, and expensive to operate at large scale.
Solution
The invention provides a two-axis solar tracking system that uses a simplified linkage structure and linear beam movement to rotate panels in both directions. It converts straight actuator motion into controlled panel rotation using a four-bar linkage mechanism supported on pillars.
Key Features
- Tracks sun in both daily (East-West) and seasonal (North-South) directions
- Uses two beams and struts connected through spherical joints
- Linear actuators convert straight motion into angular panel rotation
- Multiple panel rows can be moved using a single actuator
- Programmable electronic controller for automatic sun tracking
- Designed for easy assembly, transport, and maintenance
Benefits
- Higher solar energy output compared to fixed or single-axis systems
- Lower mechanical complexity than conventional dual-axis trackers
- Reduced installation and maintenance cost
- Suitable for large-scale solar plants and remote installations
- Improved durability and resistance to wind forces
Claim-Based Protection (Core Idea)
Claim 1 protects a two-axis solar tracker where a translating lower beam rotates the frame in the north-south direction and an upper beam rotates the solar modules in the east-west direction using a four-bar linkage structure with struts, bearings, and supporting pillars.
Overview
Solar panels generate maximum electricity only when sunlight hits them directly. However, the sun’s position changes continuously during the day and also shifts across seasons during the year.
The Problem
Most solar installations today use one of the following systems:
- Fixed-tilt panels – mounted at a permanent angle
- Single-axis trackers – move panels only from East to West
These approaches create several limitations:
- Loss of energy production
- Panels cannot face the sun properly all year. Even single-axis trackers miss the seasonal North-South movement of the sun, reducing total power generation.
- Inefficiency during winter and seasonal transitions
- When the sun is lower in the sky, sunlight strikes panels at poor angles, causing significant drop in output.
- Dual-axis trackers are impractical at scale
- Existing two-axis systems can solve the angle problem but introduce new issues:
- Heavy structures
- Complex moving parts
- High installation cost
- Expensive maintenance
- Limited number of panels per actuator
- High operating and maintenance burden
- Traditional systems use torque tubes, gearboxes, and multiple motors. These components increase failure points, downtime, and repair cost — especially in large solar farms and remote locations.
- Large solar plants require simpler mechanics
- Utility-scale projects need a system that:
- Moves many panels using minimal power
- Works reliably in wind and uneven terrain
- Is easy to transport and assemble
In Simple Terms
The industry lacks a practical solution that can fully follow the sun in both directions while still remaining affordable, simple, and reliable for large solar farms.
Current systems force a trade-off:
- Cheap systems → lower energy generation
- Accurate systems → too complex and costly
The invention addresses this gap by targeting the need for full sun tracking without the complexity and cost of conventional dual-axis trackers.
Overview
The invention provides a practical two-axis solar tracking structure that allows solar panels to follow the sun throughout the day and across seasons, while remaining simple, lightweight, and suitable for large-scale solar plants.
The Solution
Instead of using heavy rotating shafts, gearboxes, or complex pivot mechanisms found in traditional dual-axis trackers, the invention uses a smart mechanical arrangement that converts straight-line motion into controlled panel rotation.
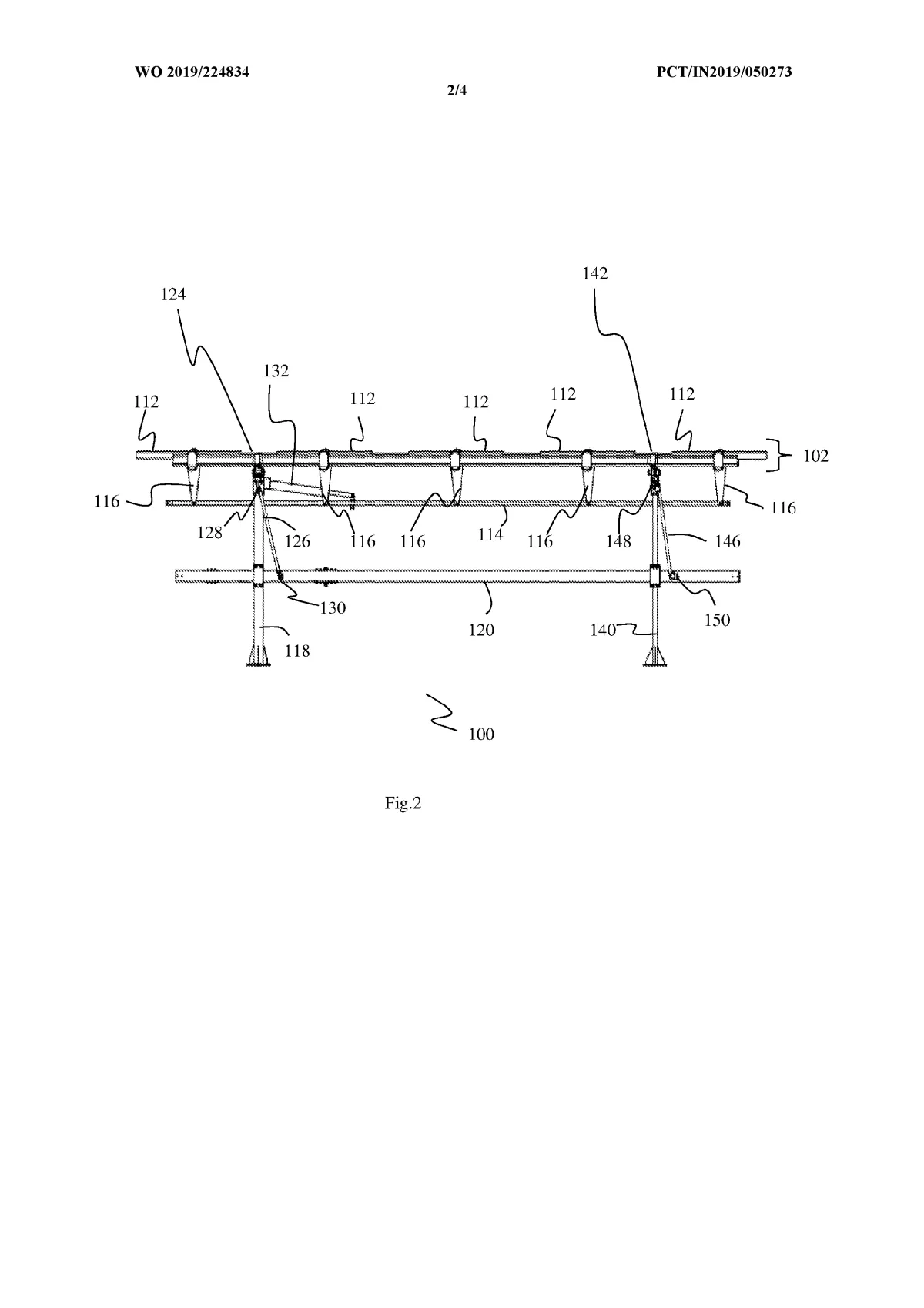
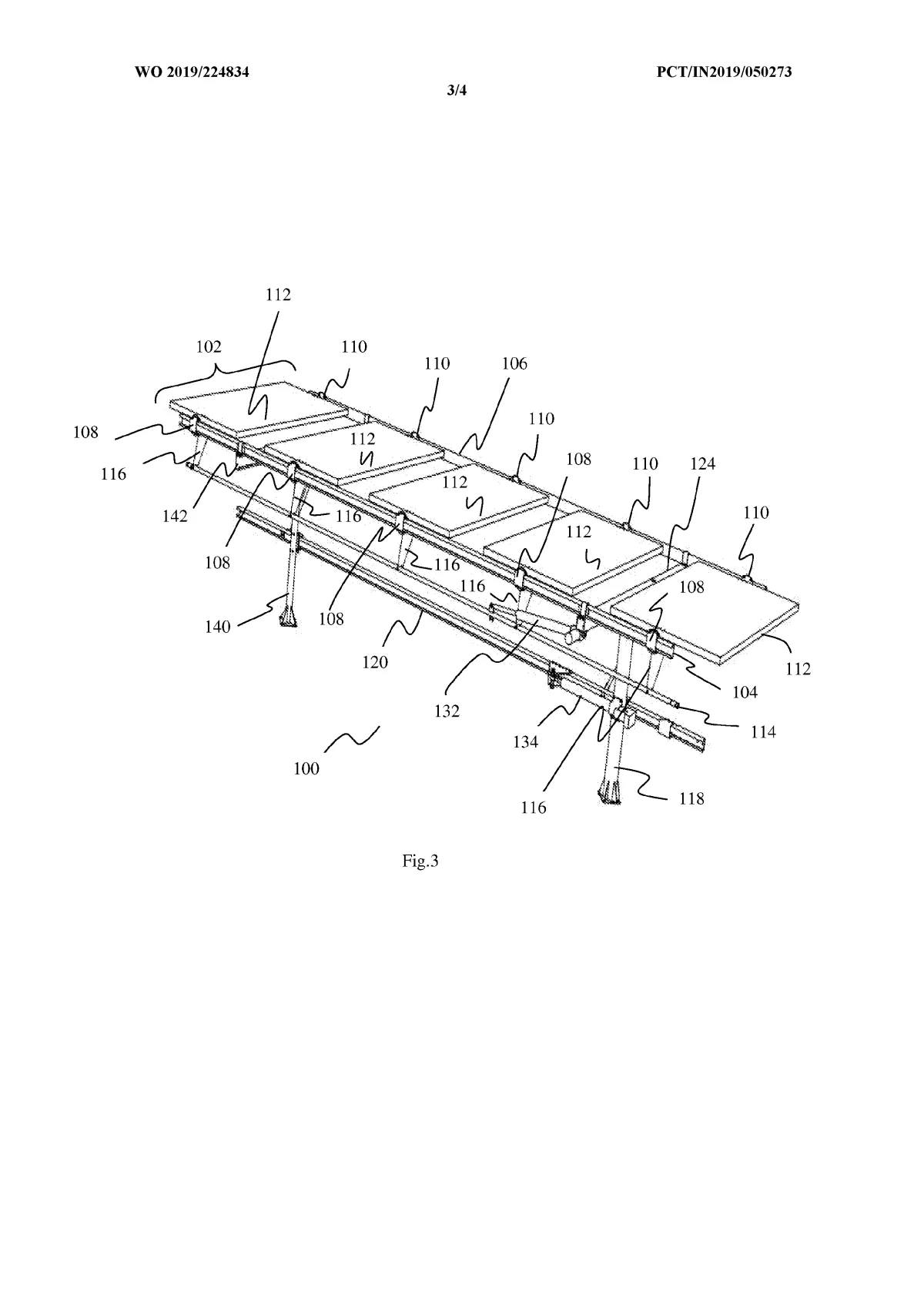
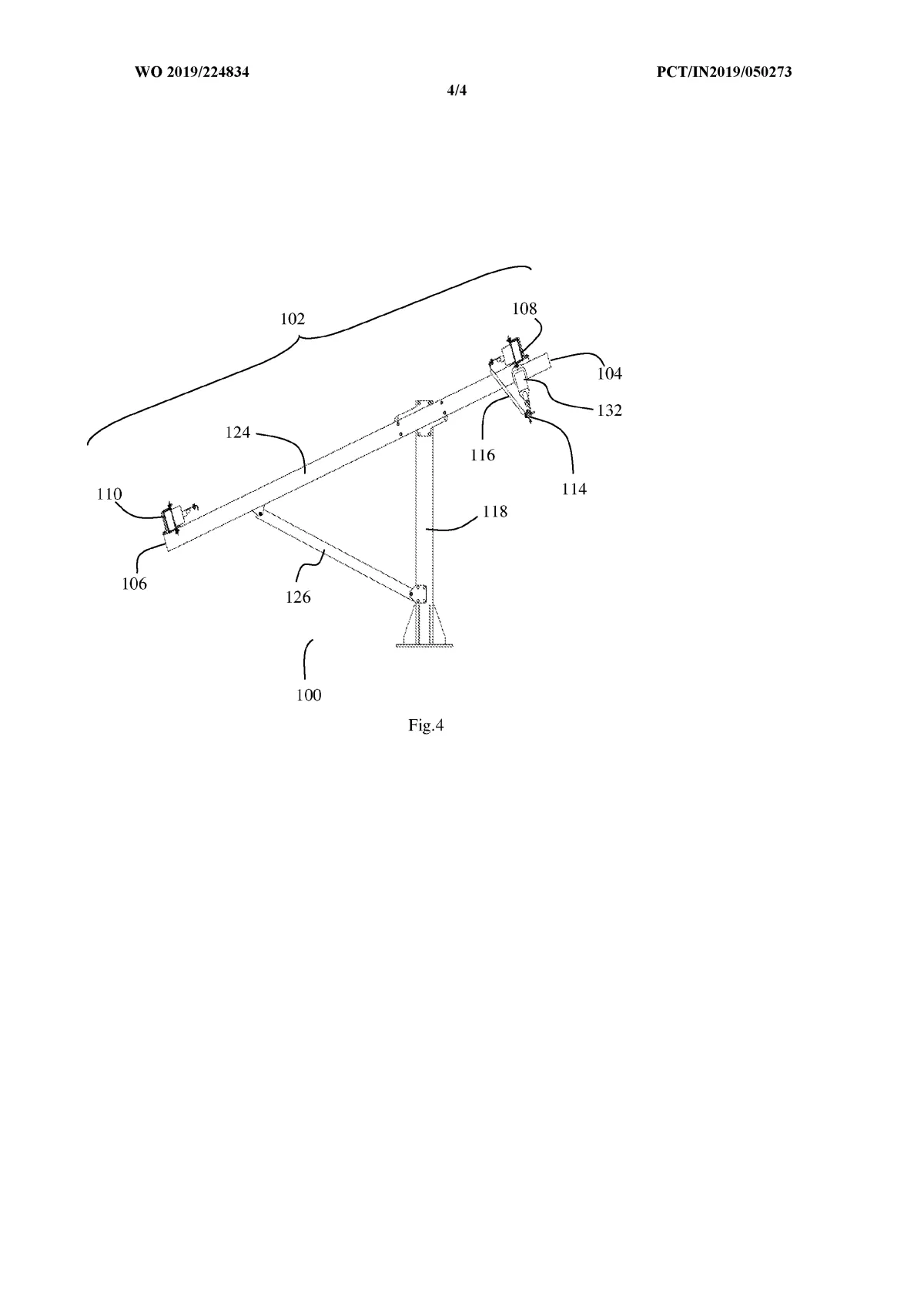
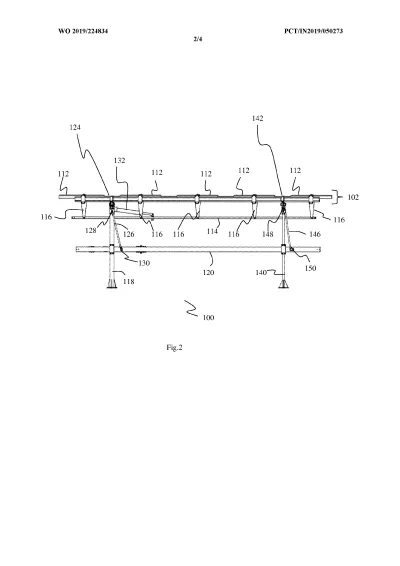
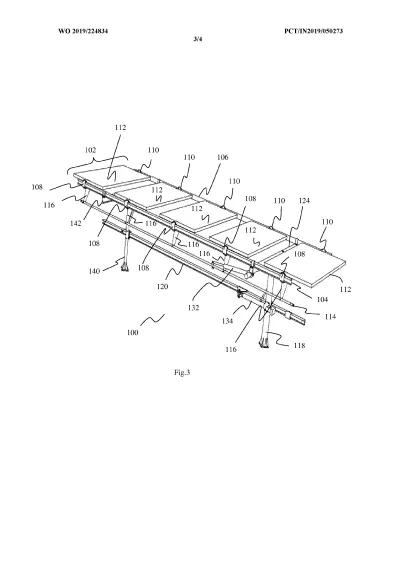
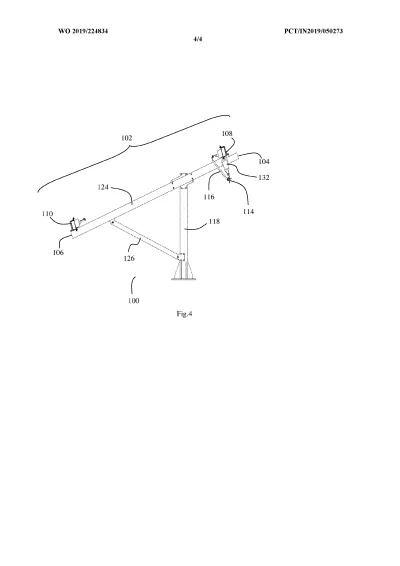
The system is built around a supported frame mounted on pillars. Two moving beams — an upper beam and a lower beam — are driven by actuators. These beams do not directly rotate the panels. Instead, they transfer motion through struts, flexible brackets, and joints arranged in a four-bar linkage structure.
- The upper beam moves in a straight line and rotates the solar modules from East to West (daily tracking).
- The lower beam slides between supporting pillars and tilts the entire frame North to South (seasonal tracking).
Because motion is transmitted through linkages rather than heavy rotating shafts, the system can move multiple panels using minimal force and fewer drive components.
How it Solves the Industry Gap
- Achieves dual-axis tracking without complex rotating assemblies
- Reduces number of motors required to operate many panels
- Allows linear actuators to move large structures efficiently
- Simplifies installation and maintenance
- Maintains structural stability and wind resistance
Operational Principle
- Actuators push or pull the beams in straight motion
- Linkages convert this motion into angular rotation
- Panels automatically face the sun at optimal angles
- A programmed controller manages tracking automatically
Practical Result
The invention delivers near full sun-following capability while keeping the mechanical design simple and scalable. It enables higher energy generation compared to fixed and single-axis systems, but without the cost and complexity normally associated with traditional dual-axis trackers.
Claim-Based Core Idea
Claim 1 protects a solar tracker where linear movement of an upper beam rotates the panels in the East-West direction, and translation of a lower beam rotates the frame in the North-South direction through a four-bar linkage mechanism supported on pillars.
Yes — the invention addresses a significant gap in existing solar tracking technology.
The Gap in Prior Art
The solar industry currently faces a trade-off between performance and practicality:
- Single-axis trackers (widely used)
- Track the sun only from East to West
- Cannot adjust for seasonal North-South movement
- Result: noticeable annual energy loss, especially in winter and transition months
- Conventional dual-axis trackers (technically accurate)
- Provide better sun alignment
- But introduce major drawbacks:
- Heavy rotating structures
- Gearboxes and torque tubes
- Multiple motors and drive shafts
- High installation and maintenance cost
- Limited scalability for large solar farms
Because of these issues, utility-scale solar plants typically avoid true dual-axis systems despite their efficiency benefits.
Core Industry Gap
There has been no practical solution that delivers:
- Full or near-full sun tracking accuracy
- Mechanical simplicity
- Low operating cost
- Suitability for large-scale deployment
In short:
The market lacked a dual-axis performance system with single-axis level practicality and economics.
How the Invention Bridges the Gap
The invention replaces complex rotational mechanisms with a linear-motion four-bar linkage structure that:
- Enables both East-West and North-South tracking
- Uses fewer drive components
- Moves multiple panels with minimal force
- Simplifies installation and maintenance
Result
It closes the long-standing gap between high-efficiency tracking and commercially viable large-scale solar deployment by combining dual-axis tracking capability with simplified mechanical architecture.
Unique Features of the Product
Dual-axis tracking using linear motion
Uses straight-line actuator movement to rotate solar panels in two directions instead of traditional rotating shafts and gear systems.
Four-bar linkage mechanism
Converts beam translation into controlled angular movement of the panel frame, enabling seasonal (North-South) and daily (East-West) tracking.
Separate motion control for frame and panels
Upper beam rotates the PV modules East-West, while a sliding lower beam tilts the entire structure North-South.
Selective flexible brackets and spherical joints
Allow smooth multi-directional movement and alignment even on uneven terrain while reducing mechanical stress.
Single actuator operation for multiple units
Multiple tracker rows or panels can be synchronized and driven using minimal motors, lowering complexity and cost.
Eliminates torque tubes and gearboxes
Reduces heavy components, mechanical losses, and maintenance requirements compared to conventional dual-axis trackers.
Wind-resistant balanced structure
Pillar-supported geometry and strut balancing help stabilize the system and lock position during high wind conditions.
Modular and easy to install
Lightweight structure designed for transport, remote installation, and quick assembly.
Programmable automatic tracking
Controlled by an electronic controller following solar path algorithms for autonomous operation.
Industries where the invention can be useful?
Utility-scale solar power plants, Commercial & industrial rooftop solar systems, Solar farms in high-irradiance regions, Government renewable energy projects, Independent power producers (IPPs), Microgrids and rural electrification projects, Solar parks in desert and remote terrains, Agrivoltaics (solar installed above farmland), Off-grid and hybrid renewable energy systems, Solar EPC and module mounting structure manufacturers,An estimate of the total addressable market?
Market Size – Total Addressable Market (TAM) The invention targets the solar tracking system segment of the global solar power industry — the hardware used to orient solar panels toward the sun to increase electricity generation. Global Solar Deployment Base The world installs roughly 350–450 GW of new solar capacity per year (utility-scale + commercial). A large and growing share of new utility-scale plants now use tracking systems instead of fixed structures because higher output improves project revenue. Tracker Hardware Spending Typical tracker system cost (structure + drives + controls): Approx. $70 – $150 per kW depending on region and design Applying this to annual installations: 350–450 GW/year × $70–$150/kW → ≈ $25 billion – $65 billion annual tracker hardware market Addressable Segment for This Patent The invention specifically competes where developers want: Higher yield than single-axis trackers Lower cost and complexity than traditional dual-axis trackers Therefore the realistic addressable opportunity includes: Utility-scale solar farms High-irradiance markets Land-constrained projects Performance-optimized commercial installations Estimated Total Addressable Market (TAM): ~$25B – $65B annually worldwide, growing with solar expansion. Commercial Interpretation Because every large solar project must choose a mounting/tracking structure, the invention participates in a fundamental infrastructure layer of the energy industry. As developers increasingly prioritize energy yield and cost per kWh, improved tracking solutions represent a recurring and expanding global market opportunity.Potential Customers/End Users. Who might benefit?
Potential Customers / End Users Primary Commercial Users Utility-scale solar farm developers Independent Power Producers (IPPs) Solar project investors and asset owners Solar EPC (Engineering, Procurement & Construction) contractors Solar park operators and O&M service providers Manufacturing & Integration Customers Solar tracker and mounting structure manufacturers Photovoltaic module mounting system suppliers Renewable energy equipment OEMs Steel structure and fabrication companies supplying solar plants Commercial & Institutional Users Large commercial and industrial facilities installing captive solar plants Warehouses, factories, and industrial campuses Airports, railways, and infrastructure operators Data centers and high-energy-consumption facilities Government & Public Sector Government renewable energy agencies Public utility companies Rural electrification and microgrid programs Defense and remote infrastructure power systems Special Application Users Agrivoltaic farm operators (solar over agriculture land) Desert and high-irradiance solar projects Off-grid and hybrid renewable energy installations Who Benefits Most Organizations seeking higher energy generation per installed panel — without the complexity and maintenance burden of conventional dual-axis trackers — would gain the greatest operational and financial advantage.Actions
Added all portfolio
| Country | Current Status | Patent Application Number | Patent Number | Applicant / Current Assignee Name | Title | Google Patent Link |
| India | Granted | 201811019035 | 449965 | Varun Sachar | A TWO AXIS SOLAR TRACKING SYSTEM TO TRACK SUN RAYS | Google patent link |
You may also like the following patent