Battery Power Management Apparatus and Method
This invention is a smart battery management system that helps ensure vehicles and other devices always have sufficient power. It works by dividing the electrical system into two parts: one powered by a primary battery that handles essential functions like the vehicle ignition or electric motor, and another powered by an auxiliary battery that supplies power to always-on or “drain” loads (such as security systems and digital components) without draining the primary battery. The system uses smart switches—including manual and remote-controlled cutoff switches—to disconnect the primary battery when it’s not needed, thereby preserving its charge. In addition, a built-in monitoring system detects low battery conditions and automatically triggers recharging (using an alternator or generator) to restore power. This approach not only maintains battery reliability and extends the overall battery life but also provides enhanced security by preventing unauthorized vehicle starts.
Problem Addressed by the Invention (Simplified):
Vehicles, especially electric and hybrid ones, rely on batteries to power crucial systems. However, when the vehicle is not in use, many circuits (like alarms, radio memory, and security devices) still draw power. This constant drain, often called a "parasitic drain," can deplete the vehicle’s primary battery, leaving it with insufficient power to start the engine or operate key components when needed.
At the same time, some circuits in a vehicle do require power even when the engine is off, such as the anti-theft systems and electronic control units. Disconnecting the battery to prevent drain would also disable these important systems, compromising safety and convenience.
This invention addresses the problem by using a dual-battery system that divides power management into two parts:
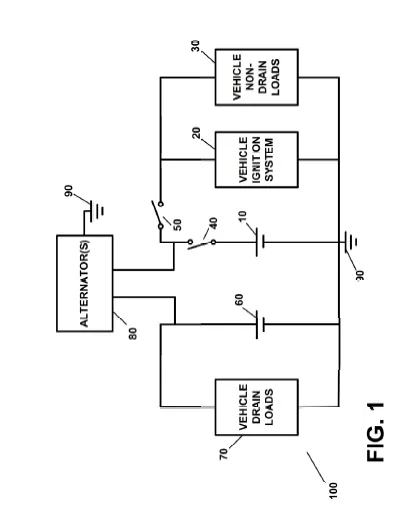
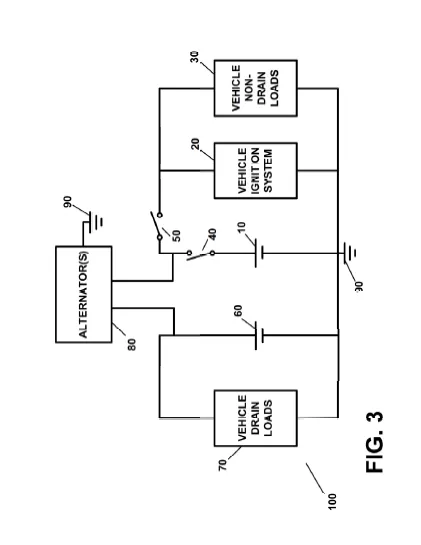
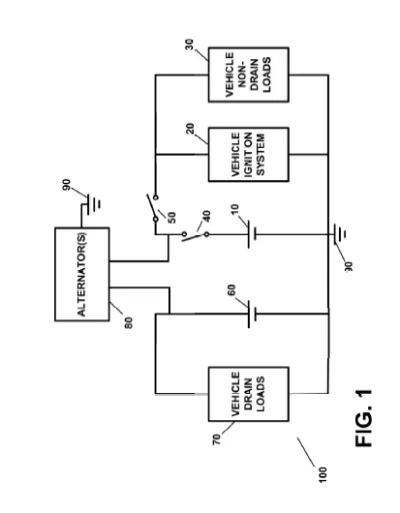
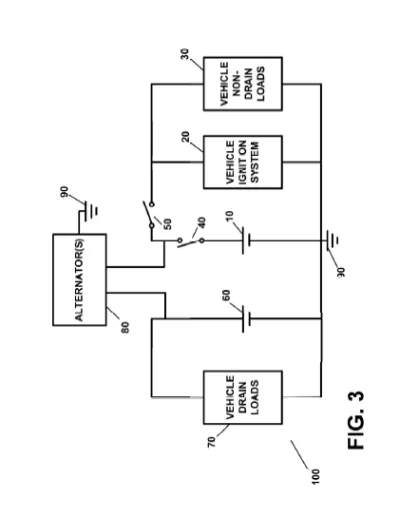
• Primary Battery: Dedicated to essential functions like starting the vehicle and powering the ignition system. This battery is isolated when the vehicle is not in use, which prevents it from being drained by non-essential circuits.
• Auxiliary Battery: Supplies power to all the non-critical or “always-on” functions (drain loads) such as security systems, computer modules, and other circuits that need constant power. This ensures these systems remain operational even when the main battery is preserved.
In addition, the invention includes smart switching and remote control mechanisms that allow the driver or a central controller to disconnect or reconnect the primary battery as needed. This helps conserve battery charge during periods of non-use while ensuring that the vehicle can quickly resume normal operation when required.
Furthermore, the system incorporates a battery monitoring component that continuously tracks the charge levels of both batteries. When the charge falls below a predefined level, it automatically triggers a recharging process using an alternator or generator. This proactive approach ensures that the batteries are recharged and ready for operation, reducing the risk of battery failure or a “dead battery” scenario.
In simple terms, the invention solves three major issues:
Preventing Battery Drain: It keeps the main battery charged by isolating it from circuits that would otherwise drain power when the vehicle is off.
Maintaining Essential Functions: It supplies constant power to critical systems through a separate auxiliary battery, ensuring that essential functions like anti-theft and key diagnostics continue to work.
Ensuring Quick Recharge: It monitors battery levels in real time and initiates recharging when needed, so the vehicle is always ready for operation.
Overall, the invention provides a comprehensive, automated solution that balances battery preservation, operational readiness, and vehicle security, addressing the common problems of battery depletion and reliability in modern vehicles.
Solution Provided by the Invention (Simplified):
The invention offers a comprehensive battery management system that effectively addresses the common problem of battery drain and power reliability in vehicles and other applications that rely on rechargeable batteries. The solution centers around a dual-battery approach combined with smart control and monitoring systems.
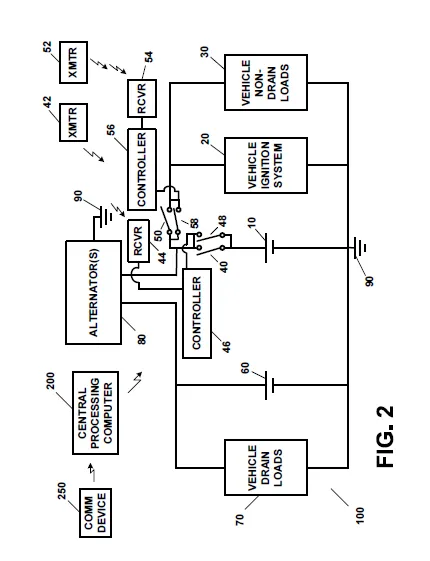
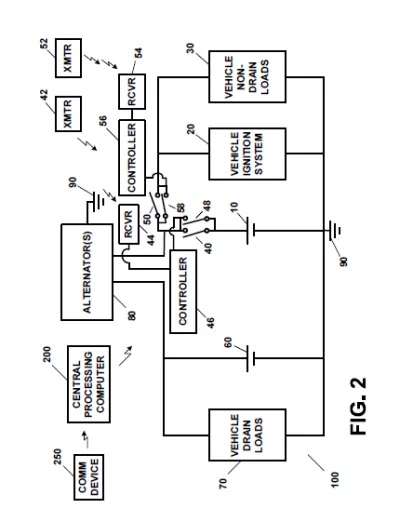
At its core, the invention uses two batteries—a primary battery and an auxiliary battery—to achieve a balance between conserving power and supplying it where it is most needed. The primary battery is dedicated to powering critical functions, such as the vehicle’s ignition system or electric motor, ensuring that the essential systems needed to start and run the vehicle are always ready. When the vehicle is not in use, smart circuits and remote-controlled cutoff switches automatically disconnect the primary battery from non-essential loads, thereby preventing it from being drained by systems that are not needed during inactivity.
Simultaneously, the auxiliary battery continuously supplies power to systems that require always-on functionality, such as security or anti-theft components, computer modules, and other electrical devices that cannot be easily turned off. This separation ensures that while the main battery is preserved for crucial operations, vital secondary systems remain powered.
To further enhance reliability, the invention incorporates a battery monitoring system that continuously tracks the state of charge of both batteries. When the system detects that the charge level drops below a predefined threshold, it automatically issues a control signal to trigger a recharging process using an alternator or generator. This recharging mechanism ensures that both batteries are replenished efficiently, so the vehicle is always prepared for operation.
Additionally, the system features remote control capabilities, enabling operators to manually or remotely disconnect and reconnect power to the batteries. This not only helps in reducing power drain during periods of inactivity but also adds an extra layer of security by preventing unauthorized use or start-up of the vehicle.
In summary, the invention solves the problem by isolating the primary battery from parasitic loads during non-use, thereby conserving its charge, while continuously supplying power to essential and non-drain functions via the auxiliary battery. The integration of real-time battery monitoring and automated recharging eliminates the risk of a dead battery and ensures seamless vehicle operation, ultimately providing a robust, efficient, and secure power management solution.
Yes, the invention addresses a major gap in the prior art.
Traditional battery systems in vehicles often use a single battery to power both critical and non-critical systems. This design creates two main issues:
• Parasitic Drain: When the vehicle is not in use, continuously powered systems (such as security devices, control modules, and other “always-on” circuits) drain the battery. In conventional designs, disconnecting the battery to prevent this drain disables important functions, leaving vehicles vulnerable to issues like failed start-ups or compromised security.
• Lack of Automated Power Management: Existing systems rarely integrate real-time battery monitoring with automated recharging. Drivers must manually manage battery connections, which is inconvenient and can result in unanticipated battery depletion. There is also limited use of remote control or intelligent switching systems that can dynamically adjust the power supply based on the state of the battery.
This invention bridges the gap by implementing a dual-battery system that separates power functions. The primary battery is dedicated to critical functions, such as vehicle ignition or driving components, ensuring that when the vehicle is idle, it remains disconnected from parasitic loads. Simultaneously, the auxiliary battery powers non-critical systems that require constant electricity. This separation preserves the primary battery’s charge while keeping essential features operational.
Moreover, the invention incorporates smart switching mechanisms—both manual and remote-controlled—that automatically disconnect the primary battery from non-drain loads when the vehicle is inactive and reconnect when needed. The system is further enhanced by a battery monitoring component that continuously tracks the state of charge of both batteries. When a low charge is detected, the system automatically triggers a recharging process using an alternator or generator to restore power to both the primary and auxiliary batteries.
By providing a comprehensive, automated approach that preserves the critical battery charge, maintains system functionality, and prevents unauthorized vehicle use, this invention effectively addresses key shortcomings in prior art. It not only prevents battery depletion due to parasitic drain but also ensures that the vehicle is ready for operation with minimal intervention from the user.
Overall, the innovative combination of dual-battery separation, intelligent switching, continuous monitoring, and automated recharging fills a crucial gap that previous designs did not address.
Unique Features of the Invention:
• Dual-Battery Architecture: The system uniquely employs two distinct batteries—a primary battery dedicated to critical vehicle functions (such as the ignition system or electric motor) and an auxiliary battery that powers non-drain loads (such as security systems and control modules). This separation minimizes battery drain during periods of inactivity while ensuring essential functions remain operational.
• Smart Switching Mechanisms: It incorporates both manual and remote-controlled switches that intelligently disconnect the primary battery from parasitic loads when the vehicle is off. This selective connection is achieved via a main cutoff switch and an ignition/On switch, ensuring that when the vehicle is inactive, the primary battery’s charge is conserved, and when needed, it automatically reconnects to resume normal operation.
• Comprehensive Battery Monitoring System: The invention features an integrated battery monitoring system that continually tracks the state of charge of both the primary and auxiliary batteries. This system detects low charge conditions and automatically sends control signals to initiate recharging, thereby preventing battery depletion and ensuring that the vehicle is always ready for operation.
• Automated Recharging Process: When low battery levels are detected, the system automatically triggers a recharging process via an alternator or generator. This automated recharging mechanism guarantees that both batteries are quickly replenished without user intervention, contributing to overall system efficiency and reliability.
• Remote Control and Connectivity: The apparatus includes remote control capabilities, allowing operators to manage the system via RF or IR signals, or over the Internet using a central processing computer. This connectivity enhances convenience, security, and allows for real-time adjustments based on battery performance.
• Voltage Stabilization and Interconnection: By employing voltage stabilizing components (such as resistors or dedicated load devices), the system can balance the voltage differences between the primary and auxiliary batteries. This ensures stable power delivery and smooth operation across the entire electrical network of the vehicle.
• Adaptability to Various Vehicle Types: The invention is designed to be versatile, making it suitable not only for conventional vehicles but also for electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and even applications involving premises or other articles that use DC power sources. This flexibility allows it to serve a wide range of market needs in automotive and power management sectors.
These unique features collectively provide an advanced, reliable, and secure battery power management solution that significantly improves the efficiency, readiness, and safety of vehicles by addressing critical power management challenges.
An estimate of the total addressable market?
Global Market Size: Approximately USD 20-30 billion by 2030 Indian Market Size: Approximately USD 1-3 billion by 2030Potential Customers/End Users. Who might benefit?
Potential Customers / End Users: • Electric Vehicle Manufacturers – Companies that design and produce electric vehicles can integrate this system to ensure reliable power management and extend vehicle range. • Hybrid Vehicle Manufacturers – Businesses producing hybrid cars can benefit from enhanced battery conservation and efficient energy use. • Automotive Component Suppliers – Firms supplying advanced automotive electronics and battery systems can incorporate this technology into their product portfolios. • Fleet Operators & Logistics Companies – Commercial fleets and logistics providers using EVs or hybrids would reduce downtime and improve operational reliability with better battery management. • Public Transportation Agencies – Operators of buses, trains, and other public transit vehicles can use the system to ensure that critical systems remain functional, even during non-operation periods. • Taxi & Ride-Sharing Services – Companies in shared mobility can benefit from extended battery life and reduced maintenance issues, contributing to more reliable service. • Charging Infrastructure Developers – Providers developing EV charging networks can enhance their offerings by integrating intelligent power management solutions. • Smart City Planners & Urban Developers – Municipalities and developers promoting sustainable urban mobility can incorporate this technology into infrastructure projects for efficient energy use. • Energy Management & Renewable Energy Companies – Businesses focusing on power storage, renewable integration, and overall energy efficiency can deploy this system in various applications. • Security & Anti-Theft System Providers – Companies offering vehicle security solutions can utilize the anti-theft benefits by ensuring the primary battery remains isolated until authorized use.Actions
Added all portfolio
| Country | Current Status | Patent Application Number | Patent Number | Applicant / Current Assignee Name | Title | Google Patent Link |
| USA | Continue | 202414057130 | N/A | JOAO, Raymond, Anthony | Battery Power Management Apparatus and Method | Google patent link |
You may also like the following patent